Multimodal Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Vascular Small Bowel Bleeding: Integrating Endoscopy, Imaging, and Pharmacologic Advances
Keywords:
- Vascular Small Bowel Bleeding, Angiodysplasia, Capsule Endoscopy, Deep Enteroscopy, CT Angiography, Argon Plasma Coagulation, Octreotide, Bevacizumab, Artificial Intelligence, Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia.
Abstract
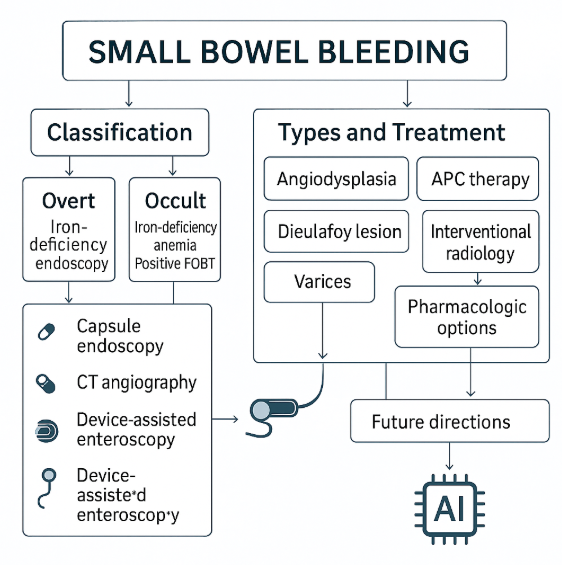
Vascular minor bowel bleeding (VSBB) constitutes a diagnostically challenging and clinically significant subset of gastrointestinal hemorrhage, especially in elderly and comorbid populations. Angiodysplasia, Dieulafoy lesions, ectopic varices, and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) are primary vascular causes. Recent advancements in endoscopic, radiologic, and pharmacologic technologies have dramatically improved the diagnostic yield and therapeutic precision in managing these lesions. Objective: This comprehensive review aims to synthesise current evidence regarding the pathogenesis, diagnostic pathways, and therapeutic strategies for VSBB, while emphasising the integration of emerging tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), genetic testing, and angiogenic profiling. Methods: An extensive review of published clinical guidelines, systematic reviews, randomised trials, and observational studies was conducted. Diagnostic algorithms and therapeutic options, including endoscopic therapies (e.g., argon plasma coagulation, sclerotherapy), radiologic interventions, pharmacologic agents (octreotide, thalidomide, bevacizumab), and surgical approaches, were critically evaluated. Special considerations for high-risk populations, including those with chronic kidney disease, HHT, and anticoagulant use, were explored. Results: Video capsule endoscopy and device-assisted enteroscopy have emerged as cornerstones for diagnosis, with computed tomography angiography offering essential support in unstable patients. Endoscopic modalities remain first-line for most lesions, while pharmacologic therapy is crucial for diffuse or recurrent bleeding. Surgical interventions, including intraoperative enteroscopy and valve replacement in Heyde’s syndrome, serve as definitive options in select patients. AI and molecular diagnostics offer transformative potential for early detection and personalized treatment. Conclusion: VSBB requires a patient-specific, algorithmic management strategy combining clinical, endoscopic, radiologic, and pharmacologic insights. Continuous innovation, interdisciplinary collaboration, and the integration of AI and genomics will be vital to advancing precision medicine in this domain.