Design And Evaluation of Biodegradable Polymeric Carriers for Targeted Drug Delivery in Albino Rats
Keywords:
- Biodegradable polymers, targeted drug delivery, PLGA, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, albino rats, nanoparticles
Abstract
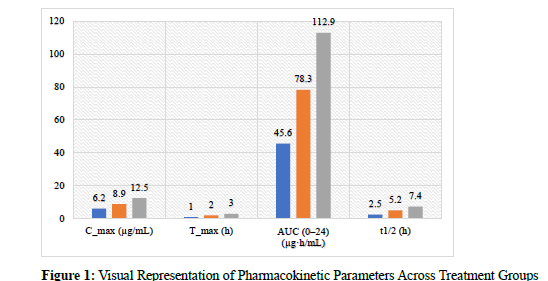
Biodegradable polymeric carriers are a potential replacement for the targeted delivery of drugs because of their biocompatibility, controlled drug release, and capacity to diminish systemic toxicity. In this research, biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles, which were designed based on PLGA, chitosan, and PCL, were developed and assessed for the targeted delivery of a model drug in albino rats. Thirty rats were adult and divided into three groups: one treated with free drug, one with the drug loaded in non-targeted carriers, and one with the drug incorporated into targeted polymeric carriers. The solvent evaporation method was utilized to prepare nanoparticles and functionalize them with folic acid for targeting tumors. Pharmacokinetic evaluation showed that the targeted carrier group had the highest C_max (12.5 μg/mL), half-life (7.4 h), and AUC (112.9 μg·h/mL) values, which reflect increased bioavailability and controlled release. Biodistribution analysis verified significantly increased drug accumulation in the tumor (9.4 μg/g) in the targeted group relative to others. Histopathological examination revealed minimal toxicity in the critical organs among the polymeric groups. Statistical testing with ANOVA confirmed significant differences (p < 0.05) in pharmacokinetic and biodistribution parameters among the groups. The results affirm that targeted biodegradable polymeric carriers represent a better option compared to conventional drug delivery in enhancing site-specific accumulation, therapeutic efficacy, and safety.